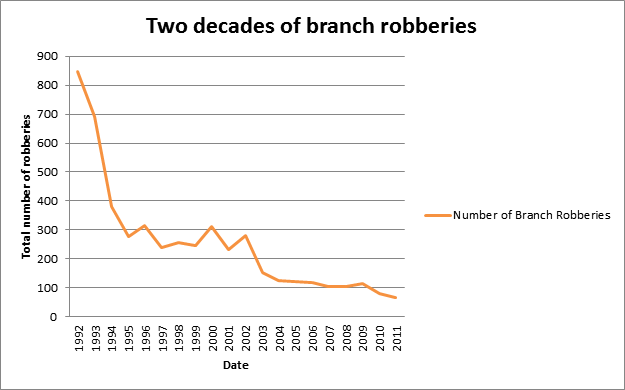
28th December 2013 The decline of the bank robber Better technology and improved security measures have cut robberies in British banks by over 90 per cent in less than two decades, new figures reveal.
Industry-wide figures show that there were just 66 such robberies in 2011 – down from 847 in 1992.
DNA spray is another common deterrent – robbers are coated with a unique, traceable material that is extremely difficult to wash off skin and can prove that a suspect was at the premises of a robbery. “Banks are working hard to confine armed robberies to the world of TV dramas," said Anthony Browne, CEO of the British Bankers' Association. "Being caught up in a bank job is a terrifying ordeal for staff and customers that can scar lives for decades. It’s great to see the number of these crimes has fallen sharply in recent years." "Anyone trying to rob a bank now faces much better CCTV, protective screens that can rise in less than a second and even special fog designed to disperse criminals. Banks will continue to work closely with each other, post offices and the police to make such raids a thing of the past.” A similar trend has been experienced in the US, according to FBI figures for 2012. Such crimes may be even more difficult (if not impossible) in the future as we move towards a cashless society. Physical currency may disappear entirely.
Comments »
|