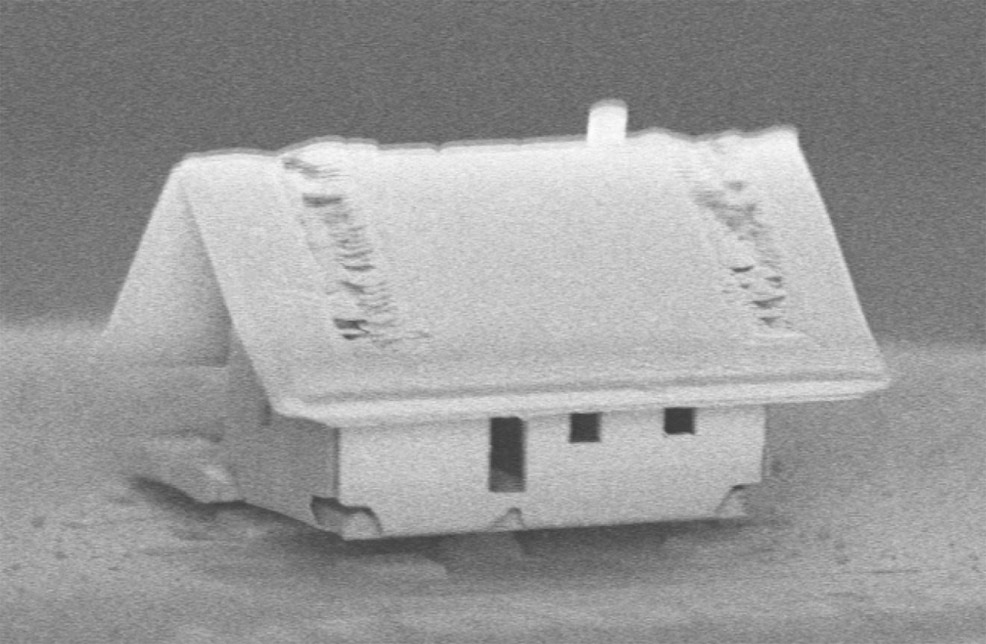
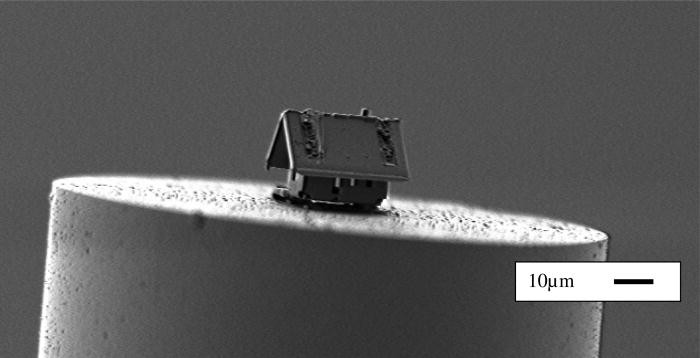
21st May 2018 World's smallest house built from nanotechnology Scientists in France have built a house on the tip of an optical fibre, with an accuracy of just two nanometres.
A nanorobotics team from the Femto-ST Institute in Besançon, France, has designed a new system that pushes the frontiers of optical nanotechnologies. Combining several existing technologies, the μRobotex nanofactory builds structures in a large vacuum chamber and fixes components to optical fibre tips with extreme accuracy. This construction system, reported in the Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, demonstrates how researchers can advance optical sensing technologies when they manipulate ion guns, electron beams and finely-controlled robotic piloting. Until now, lab-on-fibre technologies lacked robotic actuators for assembly, a problem for engineers trying to build structures on this scale. The innovation demonstrated at Femto-ST allows miniaturised sensing elements to be fitted onto fibre tips, so engineers can see and manipulate different components. With this new advancement, optical fibres as thin as a human hair could be guided into previously inaccessible locations – tiny blood vessels, for example. "For the first time, we were able to realise patterning and assembly with less than two nanometres of accuracy, which is a very important result for the robotics and optical community," said Jean-Yves Rauch, an author on the paper. The engineers combined all the technological components for nanoassembly – a focused ion beam, a gas injection system and a tiny manoeuvrable robot – in a vacuum chamber, and installed a microscope to view the process. The ion beam was used like scissors to cut the silica membrane "paper" of the house and each component was folded like origami to form a roof and walls, which were stuck in place by the gas injection system. A tiled pattern on the roof was added to provide detail and to emphasise the accuracy and flexibility of the system. The completed structure was then welded on the tip of an optical fibre, as seen in the photograph below. Two engineers worked at multiple computers to control the process. Many steps are already automated – but in the future, the team hopes to automate every robotic stage of assembly. They are now researching how to push the limits of the technology further still, by building even smaller structures and fixing these onto carbon nanotubes, only 20 nanometres in diameter.
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|