1st August 2018 Nanotechnology and innovation in vehicle manufacture A guest piece by Giles Kirkland.
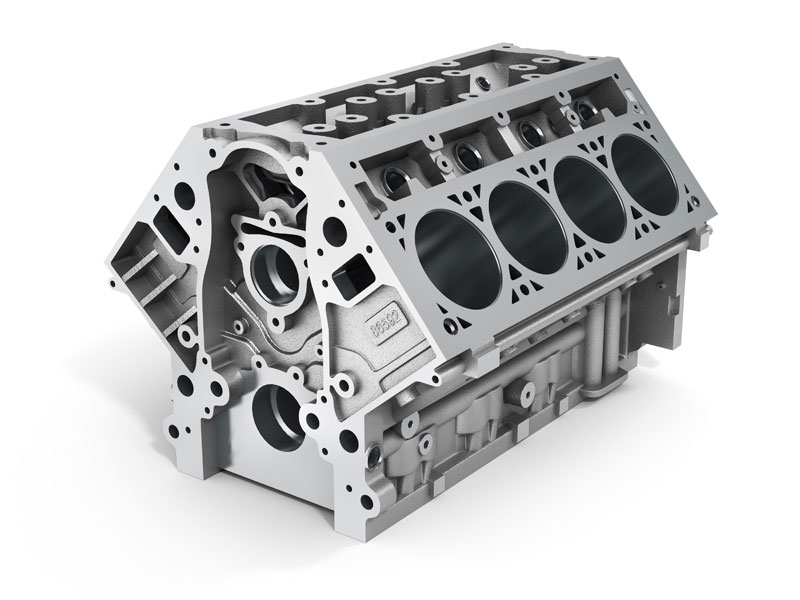
Nanotechnology refers to the production and application of materials at an atomic or molecular scale. While the concept of manipulating materials at an infinitesimal scale was formulated in the 1950s, it was only in the early 2000s that these scientific forays gained a foothold in commercial manufacture. Today, thousands of nanotechnology-dependent products are available to consumers, with new ones being developed every week. Yet despite having delivered many breakthroughs in mainstream manufacture and industrial design, we are only just beginning to see the technology's true potential when it comes to the automotive industry. Why is nanotechnology so significant to the automotive industry? Vehicles present us with a number of interesting engineering challenges. They must be lightweight enough to permit rapid acceleration and deceleration, but also strong enough to withstand those forces. Engines, in particular, require materials that afford a combination of durability and flexibility. There is also the aesthetically-driven demand for materials that are both pleasing to the eye and resistant to the constant pressures of driving and human contact. For the vast majority of the history of car design, the story of innovation revolved almost solely around seeking better solutions for these engineering conundra. Then the potential of nanotechnology came to light. Stronger, lighter and more durable than conventionally produced materials, nanomaterials are uniquely positioned to meet the rigour and complexity demanded by advanced vehicle designs. Improved engine efficiency and durability Nanomaterials Car engines undergo huge stresses. They operate at high temperatures and withstand constant friction and motion. Nanomaterials offer new ways to deal with these operational constraints. For example, they can be used to fundamentally alter the properties of aluminium. For many years, iron engine blocks were the industry standard, but today the majority of new small engines use aluminium. This is far lighter than iron (typically half the weight) and therefore provides better handling and fuel efficiency. Aluminium has drawbacks, though – it is weaker than iron and less resistant to heat. Nano-aluminium, on the other hand, could combine the benefits of both – engineered at the atomic level to be stronger and more durable than iron, while also retaining the lightweight properties of traditional aluminium. As well as engine blocks, it could be used in other parts requiring more sturdy materials (especially cylinder bores), making the engine lighter than ever.
Nanofluids and nanocoatings New kinds of fluids are being developed to improve conventional ones, such as lubricant. Nanofluids offer ways to enhance lubrication by permitting much greater control over particle shape, size and concentration (three vital determinants affecting wear and friction in a vehicle). For example, copper and gold nanoparticles show great promise for use in liquid protective films, which could enhance conventional oil-based lubricants. Nanocoatings also show great potential as a way to improve engine efficiency. Protective outer layers for engine components are being developed that are made up of nanoparticles of ceramic. Taking advantage of ceramic's unique thermal and friction properties, these new layerings offer extraordinary potential for reducing abrasion and wear. Engines in the future won't just be constructed of lighter and stronger nanometals; they will also be enhanced through uniquely heat, wear and friction-resistant nanomaterials. The end result will be greatly improved efficiency and durability. Safer and more efficient fuels Hydrogen fuel cells As fossil fuel-powered cars continue their journey to obsolescence, new fuel alternatives are now receiving considerable attention. Increasingly efficient and with costs improving, fuel cell technology is one possibility with considerable market potential. Because fuel cells are hydrogen-dependent, research is going into new materials capable of enhanced hydrogen storage and delivery. Nanotechnology offers a novel solution for storing this element in a semi-solid state. Carbon nanotubes, for example, are exceptionally good as a porous substrate. A lot more research is still needed, but in the future this looks set to provide radical new methods of safe, inexpensive hydrogen fuel cell storage. Battery enhancement Nanotechnology can also enhance the cathode materials within batteries, greatly increasing their efficiency. For example, nanoparticles of silicon may be used to create a new generation of lithium silicon batteries. Not only would such batteries provide an order of magnitude improvement in their capacitance, they'd also be cheaper and less environmentally harmful to produce. Cars which look better for longer Automotive coating Conventional outer clearcoat paint layers are among the most vulnerable aspects of a car's aesthetic elements, particularly if exposed to harsh weather or environmental conditions. As such, there's a strong market for materials that maintain the paint layer's lustre for as long as possible. Nano-sized inorganic fillers can be employed to create a finish that is exceptionally smooth. The small particle size and resulting huge surface area create an outer coat that is both extremely hard and highly elastic. These nanoparticle coatings also exhibit the desirable property of being almost completely transparent. The end result is a surface that is both optimised for a high shine finish and intrinsically scratch-resistant. A win-win! Further into the future – perhaps by 2050 – coatings might be capable of changing colour on-demand. At the touch of a button, the entire vehicle could become red, blue, green or whatever colour you desired. Or perhaps it could feature a customised logo, pattern or some other design. The windows could also be programmed to auto-tint in bright sunlight.
Interior fabrics Consumers don't just expect high performance from vehicles on the market; they're also looking for interior fabrics and textiles that are both comfortable and pleasing to look at – not just one week after purchase, but throughout the car's operational lifetime. This is no small challenge! Through nanotechnology, new textiles are being developed to be self-cleaning, anti-bacterial, fire retardant and highly durable. For example, anti-microbial and odour-resistant agents such as silver and titanium oxide can be embedded directly into fabrics. The result is a non-toxic, long-lasting fabric that is capable of oxidising microorganisms on a permanent basis. Given its wide variety of applications, nanotechnology looks set to transform vehicle manufacture in the future. The novel properties of nanoscale materials won't just give us new ways to answer those ever-present engineering challenges of improved engine efficiency and better fuel sources. It'll also open up the possibility of cleaner, more durable and just plain prettier aesthetic elements. It'll be exciting to see what cars look like when all these technologies come to fruition!
Gilles Kirkland is a car expert and all-round motoring enthusiast. He can be followed on Twitter @GilesKirkland
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|