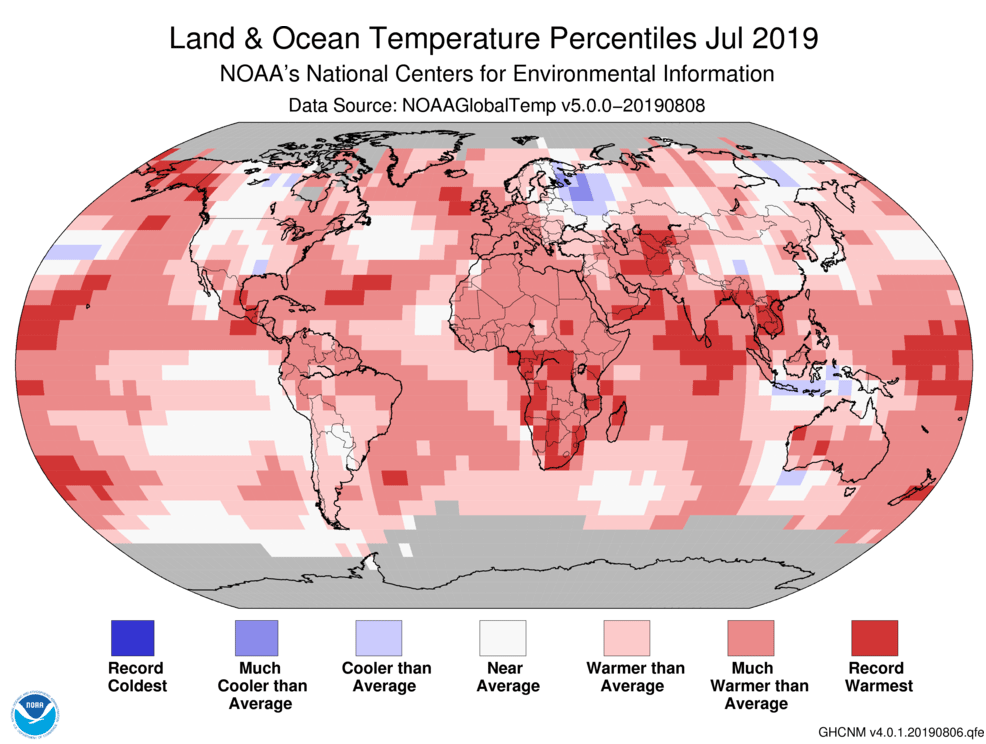
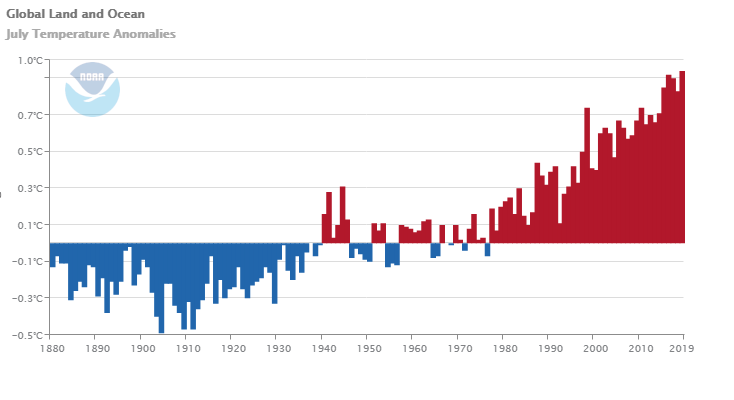
21st August 2019 July 2019 was hottest month on record globally The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reports that July 2019 was the hottest month on record globally, at 0.95°C (1.71°F) above the 20th century average.
Much of the planet sweltered in unprecedented heat in July, as temperatures soared to new heights during the hottest month ever recorded. The record warmth also shrank Arctic and Antarctic sea ice to historic lows. The average global temperature in July was 0.95°C (1.71°F) above the 20th-century average of 15.8°C (60.4°F), making it the hottest July in the 140-year record, according to scientists at NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information. The previous hottest month on record was July 2016. Nine of the 10 hottest Julys have occurred since 2005 – with the last five years ranking as the five hottest. Last month was also the 43rd consecutive July and 415th consecutive month with above-average global temperatures.
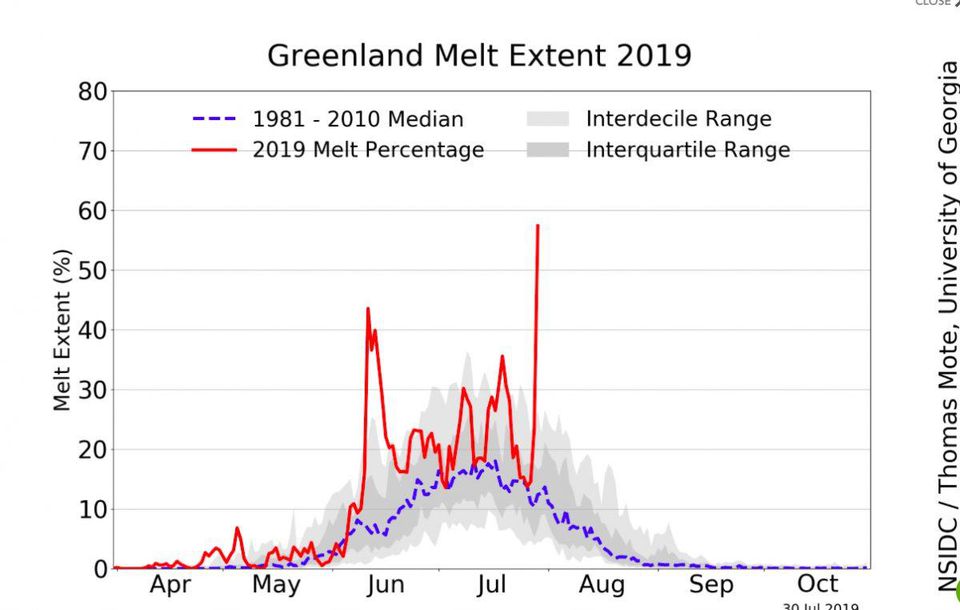
The seven month period from January through July also produced a global temperature that was 0.95°C (1.71°F) above the 20th-century average of 13.8°C (56.9°F), tying with 2017 as the second hottest year-to-date on record. It was the hottest year to date for parts of North and South America, Asia, Australia, New Zealand, the southern half of Africa, portions of the western Pacific Ocean, western Indian Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. In the Arctic, sea ice set a new record low for July, running 19.8% below average – surpassing the previous historic low of July 2012. Danish polar research institution Polar Portal reported a huge spike in Greenland ice loss, with 11 billion tons melted in a single day and a total of 197 gigatonnes in July. In the Antarctic, sea ice coverage was 4.3% below the 1981-2010 average, making it the smallest for July in the 41-year record.
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|