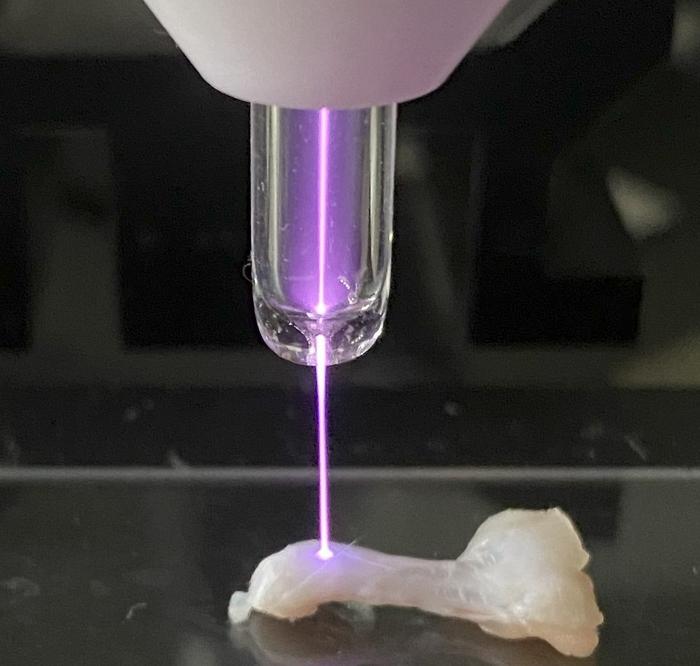
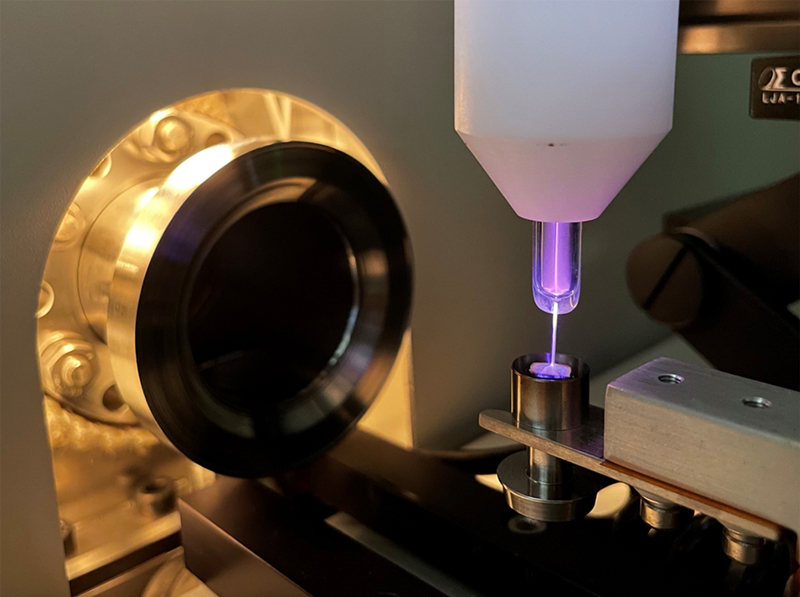
22nd May 2024 Microplasma device enables faster healing of injuries Scientists in Japan report a substantial acceleration of tendon repair, using helium plasma jet therapy.
The Achilles tendon, located at the back of your ankle, is the largest ligament in the human body. Despite its size and strength, it can be surprisingly vulnerable to tears and ruptures, with many such injuries involving sports enthusiasts in their 30s or 40s. Surgery might be required, and a prolonged period of rest, immobilisation, and treatment can be difficult to endure. Seeking to shorten the recovery time, a research team at Osaka Metropolitan University in Japan has been developing a new technique based on the application of "non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma". Their study, published this month in the journal PLOS ONE, is the first to show that such plasma irradiation can accelerate tendon repair. The team ruptured and then sutured the Achilles tendon of lab rats. For one group of rats, the sutured area was irradiated with a helium plasma jet. The plasma-irradiated group exhibited faster tendon regeneration and increased strength at two, four, and six weeks after surgery compared to the untreated group.
Notably, the plasma-treated tendons demonstrated more than double the tensile strength of untreated tendons just two weeks post-surgery. This remarkable improvement indicates that the healing process in the plasma-treated group was essentially twice as fast during this early stage. "We have previously discovered that irradiation of non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma has the effect of promoting bone regeneration," explains Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda. "In this study, we discovered that the technology also promotes tendon regeneration and healing, showing that it has applications for a wide range of fields. Combined with current tendon treatments, it is expected to contribute to more reliable tendon regeneration and shorter treatment time." We are a long way from the kind of futuristic medical devices witnessed in science fiction novels and TV shows like Star Trek. But this innovative plasma therapy brings us a step closer to such advancements. With ongoing research and development, what seems like a futuristic fantasy today might one day become a standard medical practice.
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|
||||||