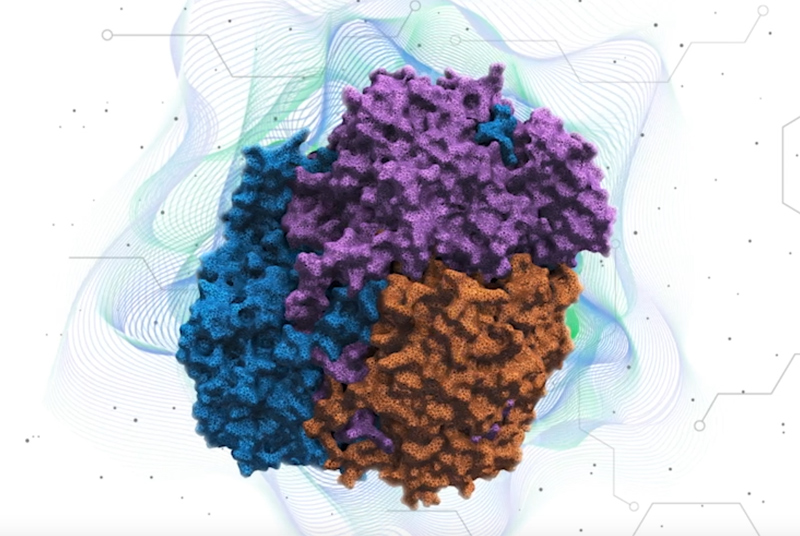
21st May 2025 New therapy aims to make muscles "more youthful" A novel treatment could restore muscle strength, offering hope for those with degenerative conditions and age-related muscle loss.
Juvena Therapeutics, a biotechnology company based in Palo Alto, California, has commenced its first human trial of JUV-161, a pioneering therapy designed to regenerate muscle tissue. This development could mark a significant step forward in addressing muscle-wasting diseases and the natural decline in muscle mass associated with aging. JUV-161 is a fusion protein therapy, which means it combines multiple functional parts of human-derived proteins into a single, engineered molecule designed to boost muscle repair. It targets the restoration of muscle health by activating the AKT signalling pathway, which is crucial for cell survival, growth and metabolism. Its primary mechanism of action is derived from an engineered version of Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF2) – a naturally occurring protein involved in growth and development. Unlike existing treatments that focus on genetic manipulation or RNA-targeting, JUV-161 aims to reinstate the body's natural protein signalling to youthful levels. This approach has earned it the moniker "insulin for muscle" among researchers. JUV-161 is the first drug candidate to emerge from Juvena's proprietary platform, JuvNET – an AI-powered system that maps the regenerative potential of proteins secreted by stem cells. By analysing enormous datasets with machine learning, JuvNET identifies proteins with the ability to repair tissue and restore healthy function. In addition to JUV-161, the platform is being used to develop other biologics, including a treatment for obesity that promotes fat loss without suppressing appetite.
The therapy will initially be tested on healthy adult volunteers in Australia, following approval from the country's Human Research Ethics Committee. This Phase I trial will assess the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of JUV-161. The results will then be used to inform subsequent studies targeting specific conditions, including Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1) and sarcopenia. DM1 is a genetic disorder characterised by progressive muscle degeneration, affecting 3.6 million people worldwide. Currently, there are no FDA-approved treatments for this condition. JUV-161 has received Orphan Drug status from the FDA for DM1, highlighting its potential to address this unmet medical need. Preclinical studies have shown promising results, with JUV-161 improving muscle strength, endurance, and metabolism in animal models. These findings suggest the therapy could not only benefit those with DM1 but also individuals experiencing age-related muscle loss. Looking ahead, Juvena Therapeutics plans to initiate Phase II trials in 2026, focusing on patients with congenital DM1 and sarcopenia. The company envisions JUV-161 as a weekly subcutaneous injection, potentially allowing patients to administer the treatment at home, similar to insulin therapy for diabetes. If successful, this innovative approach to muscle regeneration could transform the management of muscle-wasting diseases and age-related muscle decline, offering a new avenue for enhancing quality of life and longevity. "JUV-161 is a natural endocrine protein therapy that will help restore critical protein signalling in diseased muscle to more youthful, healthy levels, so that we can restore muscle health and ultimately restore the quality of life of individuals living with many indications where muscle loss reduces the quality of life or lifespan," said Dr. Hanadie Yousef, CEO and co-founder of Juvena.
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|
||||||