25th May 2025 Veo 3 sets a new benchmark for AI video generation Google DeepMind has unveiled Veo 3, a stunning leap forward in generative video AI. The company also announced upgrades to Gemini 2.5 Pro, its flagship language model.
In the late 2010s, AI-generated media began as a curiosity – amusing, occasionally uncanny, and often flawed. Websites like ThisPersonDoesNotExist.com and WhichFaceIsReal.com amazed Internet users by generating endless, photorealistic headshots of non-existent people. By 2023, generative AI moved into video, producing surreal clips like the now-infamous "Will Smith eating spaghetti" – a chaotic attempt that fascinated viewers more for its novelty than any realism. Just a few years later, the landscape has changed dramatically. This week, Google DeepMind launched Veo 3, the latest version of its video generation model – demonstrating that the field continues to advance at breakneck speed. Veo 3 delivers a major qualitative leap over earlier systems. While OpenAI's Sora impressed us with lifelike video scenes, Veo 3 goes even further. It can render clips up to 4K (3840 × 2160 pixels, or four times the resolution of full-HD), with emotionally expressive faces, lip-synced dialogue, and multi-layered environmental audio – all while maintaining consistent lighting, camera angles, motion, and physical realism. Whether generating a person walking through a street market or a crowded indoor space, the model produces results that look and sound eerily convincing.
What sets Veo 3 apart is its nuanced handling of human expressions and body language. Earlier models often produced robotic gazes or unnatural-looking poses, but Veo 3 generates expressions and movements that align with the tone and context of each scene. It also enhances depth of field and background activity, making the visuals feel more authentic. Google hasn't disclosed the exact data used for training Veo 3. However, there is speculation that the company drew upon its massive internal datasets – especially content from YouTube, which Google has owned since 2006, and which now hosts billions of videos. Some researchers also suspect that Google incorporated multi-modal sources like Reddit threads, subtitles, and transcribed audio, allowing the model to learn from a wide range of formats and topics. DeepMind likely built Veo 3 using a transformer-based architecture, similar to diffusion models, but specifically adapted for learning spatio-temporal patterns. Rather than generating single frames, the model learns how each frame should transition smoothly to the next. Veo 3 probably follows a multi-stage pipeline: starting with rough sketches and gradually refining each frame to add detail, facial precision, motion, and sound synchronisation. It aligns visual, audio, and text prompts with a high degree of accuracy, enabling users to describe complex scenes and receive rich, consistent results.
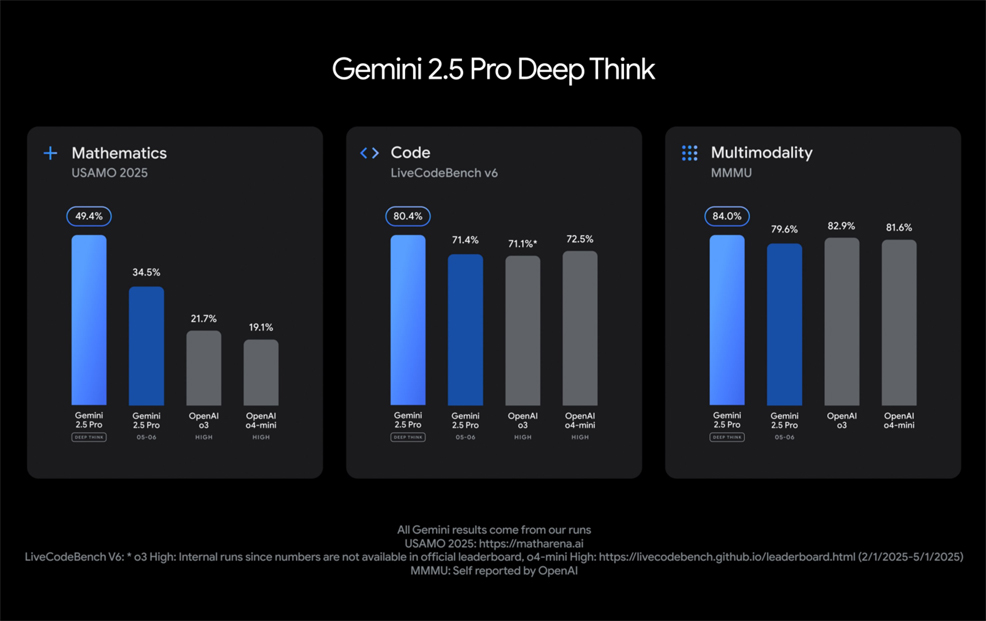
Alongside Veo 3, Google also introduced a major upgrade for Gemini 2.5 Pro, its flagship multimodal model. This includes an experimental "Deep Think" mode, designed to improve reasoning on complex tasks such as maths and coding. Gemini 2.5 Pro now supports native audio output for more natural interactions, and its performance has improved across the board. It currently leads on major benchmarks such as WebDev Arena and LMArena, and integrates more closely with Google Search – helping to reduce hallucinations and improve the overall reliability of responses. While these advances have excited many in the tech community, they also raise serious concerns. Critics warn that tools like Veo 3 could enable more convincing deepfakes, misinformation, and identity theft. For example, scammers might soon be able to create photo-realistic videos of a family member being held hostage in order to defraud elderly victims – a disturbing tactic that could devastate lives. Filmmakers, voice actors, and visual artists also fear job losses and the erosion of creative professions. Legal experts have voiced concerns about intellectual property violations, especially when AI models imitate styles, voices, or likenesses based on copyrighted works. These risks are intensifying calls for more regulation, transparency, and accountability in training and deploying such technologies. Google has emphasised that it built Veo "with responsibility and safety in mind." The company blocks harmful requests and results, tests how new features might affect safety, and employs both internal teams and external experts to identify and fix problems before public release. To further mitigate risks, videos made with Veo will be marked using SynthID, Google's watermarking and detection system for AI-generated content. Veo's outputs also undergo safety evaluations and memorisation checks to reduce issues related to privacy, copyright infringement, and bias. These safeguards show a growing industry awareness of ethical issues – but critics argue that regulation and transparency must keep pace with the technology. Amid these challenges and opportunities, Veo 3 shows that AI isn't slowing down. At the start of 2025, some analysts predicted a lull in generative AI progress – citing market fatigue and diminishing returns. Clearly, that plateau has yet to be reached. Instead, advances like Veo 3 confirm that AI continues to follow an exponential path – reshaping creativity, communication, and even our perception of reality.
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|
||||||