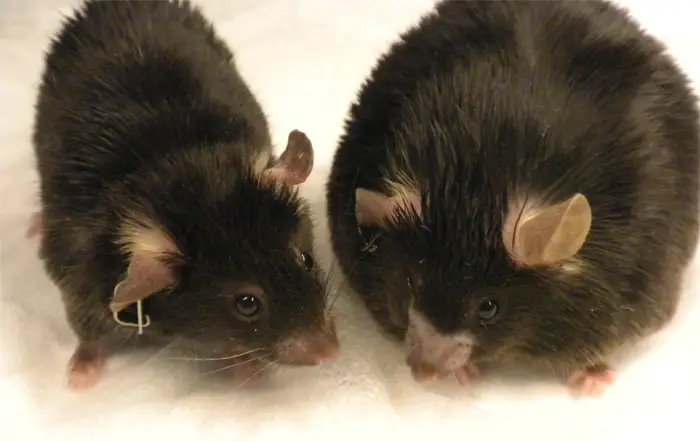
7th March 2013 Researchers discover gene that causes obesity in mice Researchers have discovered that deleting a specific gene in mice prevents them from becoming obese, even on a high fat diet, a finding they believe may be replicated in humans.
"When fed a diet that induces obesity, these mice don't get fat," said Professor James McManaman, Ph.D., lead author of the two-year study and vice-chairman of research for Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "It may be possible to duplicate this in humans, using existing technology that targets this specific gene." The research team created a strain of mice without the Plin2 gene which produces a protein that regulates fat storage and metabolism. They immediately found that the mice were resistant to obesity. Usually, mice fed a high fat diet will eat voraciously, yet these showed an unusual restraint. Not only did they eat less, they were more active. Their fat cells were also 20 percent smaller than typical mice and did not show the kind of inflammation usually associated with obesity, the study said. Obesity-associated fatty liver disease, common in obese humans and rodents, was absent in the mice without the Plin2 gene. "The mice were healthier," McManaman said. "They had lower triglyceride levels, they were more insulin-sensitive, they had no incidents of fatty liver disease and there was less inflammation in the fat cells." The absence of the gene may cause fat to be metabolised faster, he said. "Now we want to know why this works physiologically," McManaman said. "We want to better understand how this affects food consumption." According to the study, understanding how Plin2 is involved in the control of energy balance will provide new insights into "the mechanisms by which nutrition overload is detected, and how individuals adapt to, or fail to adapt to, dietary challenges." The consequences for people are highly significant, since they also possess the Plin2 gene. "It could mean that we have finally discovered a way to disrupt obesity in humans," he said. "That would be a major breakthrough." Obesity is a leading preventable cause of death worldwide, with increasing prevalence in adults and children, and authorities view it as one of the most serious public health problems of the 21st century. Of all countries, the U.S. has the highest rates. From 13% in 1962, cases have steadily increased, reaching 36% of American adults in 2010. This rate is projected to reach 42% by 2050.
Comments »
|