22nd November 2015 Genetically modified salmon approved by FDA For the first time, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved genetically modified fish for human consumption.
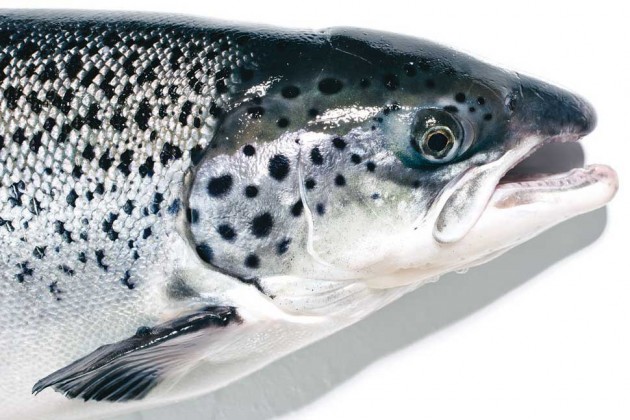
AquaBounty Technologies, Inc., a biotechnology company focused on enhancing productivity in aquaculture, announced this week that the FDA has approved its application for the production, sale and consumption of "AquAdvantage Salmon". This Atlantic salmon has been genetically enhanced to reach market size in less time than conventional farmed Atlantic salmon. Ronald Stotish, Ph.D., CEO of AquaBounty, commented: "AquAdvantage Salmon is a game-changer that brings healthy and nutritious food to consumers in an environmentally responsible manner without damaging the ocean and other marine habitats. Using land-based aquaculture systems, this rich source of protein and other nutrients can be farmed close to major consumer markets in a more sustainable manner." The U.S. currently imports over 90% of its seafood – and more specifically, over 95% of the Atlantic salmon it consumes. AquAdvantage Salmon will create the opportunity to grow an economically viable, domestic aquaculture industry. Through greater efficiency and localised production, AquaBounty claims it can increase productivity while reducing the costs and environmental impacts of current salmon farming operations. Land-based aquaculture systems can provide a continuous supply of fresh, safe, traceable and sustainable GM salmon to communities across the U.S. and do so with a lower carbon footprint. This offers an alternative approach to fish farming that does not exploit the oceans. Jack Bobo, Senior Vice President and Chief Communications Officer at parent company Intrexon, stated: "The U.S. Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee encourages Americans to eat a wide variety of seafood, including wild caught and farmed, as part of a healthy diet rich in healthy fatty acids. However, this must occur in an environmentally friendly and sustainable manner. FDA's approval of the AquAdvantage Salmon is an important step in this direction."
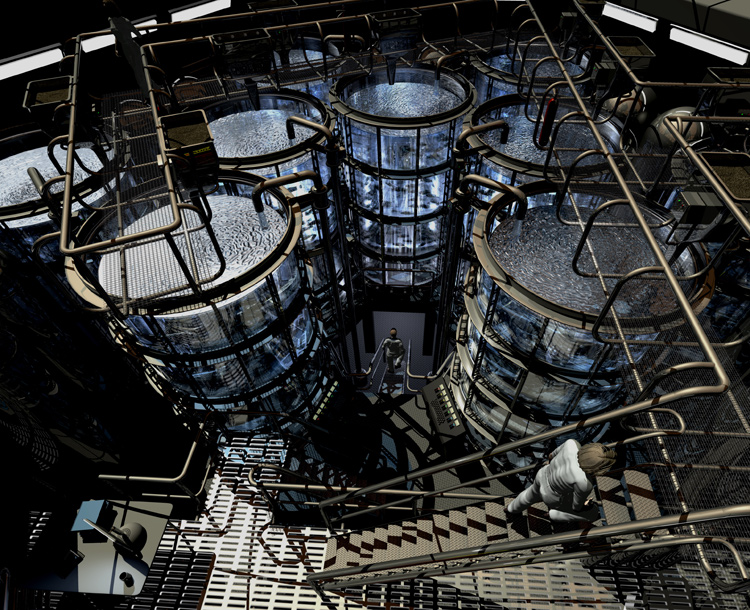
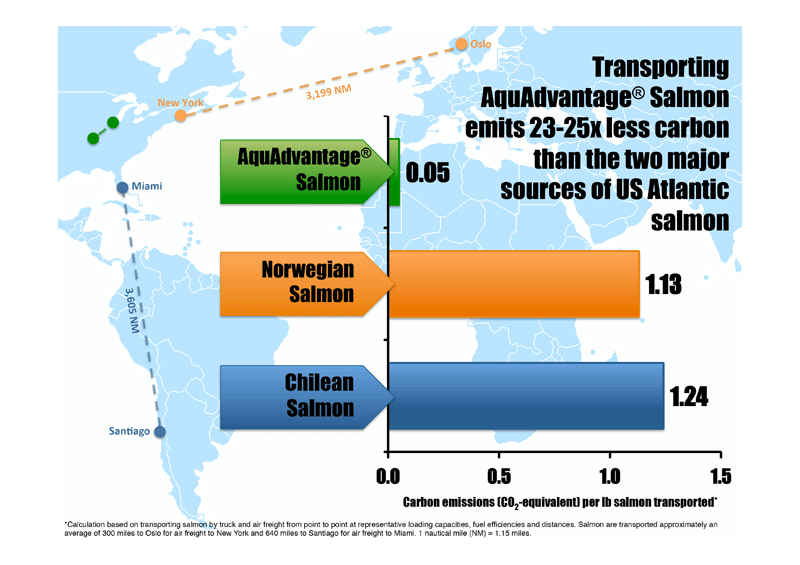
The AquAdvantage fish program is based on a molecular modification that results in more rapid growth during early development. A gene responsible for growth hormone regulation is taken from a Pacific Chinook salmon, combined with a promoter from an ocean pout, then added to the Atlantic salmon's 40,000 genes. This makes it grow year-round, instead of only during spring and summer, without affecting its ultimate size or other qualities. The GM fish grows to market size in 16 to 18 months, rather than three years. The AquaAdvantage program has other qualities that improve its sustainability credentials. The fish require 25% less feed than other Atlantic salmon on the market today. When farmed in land-based facilities close to major metropolitan areas, they will travel only a short distance to the consumer. Not only will this make them the freshest fish on the market, it will significantly cut the transportation distance from farm to table. Unlike salmon imported from Norway and Chile that travel thousands of miles by airfreight and are then trucked to markets, AquaBounty's salmon will have a carbon footprint that is 23-25 times less.
The FDA determined that the approval of the GM technology would not have a significant environmental impact, because of multiple and redundant measures taken to contain the fish and prevent their escape into the wild. These measures include a series of physical barriers placed in the tanks and in the plumbing that carries water out of the facilities to block the eggs and fish. Furthermore, the AquAdvantage Salmon are reproductively sterile, so that even in the highly unlikely event of an escape, they would be unable to interbreed or establish populations in the wild. The FDA will maintain regulatory oversight of the production and facilities and will conduct inspections to confirm these containment measures remain adequate. Despite a lengthy and detailed review process, however, the FDA's approval has provoked an angry response from some, who have questioned the safety aspects and object to the fact that no labelling will be required to indicate the fish were genetically engineered. The Centre for Food Safety (CFS), a non-profit organisation working to protect human health and promote organic food methods, has already announced plans to sue the FDA and prevent the modified salmon being sold in the U.S. "The review process by FDA was inadequate, failed to fully examine the likely impacts of the salmon's introduction and lacked a comprehensive analysis," said executive director Andrew Kimbrell in a press statement, citing the 2 million people who filed public comments in opposition, the largest number of comments the FDA has ever received on any issue. "This decision sets a dangerous precedent, lowering the standards of safety in this country. CFS will hold FDA to their obligations to the American people." Globally, traditional "capture" fisheries have been on a plateau since the late 1980s due to unsustainable yields. Aquaculture is now among the fastest growing industries in the agricultural sector and is projected to supply the majority of the world's seafood by the mid-2020s, overtaking wild catch harvests by weight. With fisheries collapsing from over-exploitation, pollution, climate change and other problems, aquaculture is likely to become a sustainable and vitally important industry of the 21st century.
Comments »
|