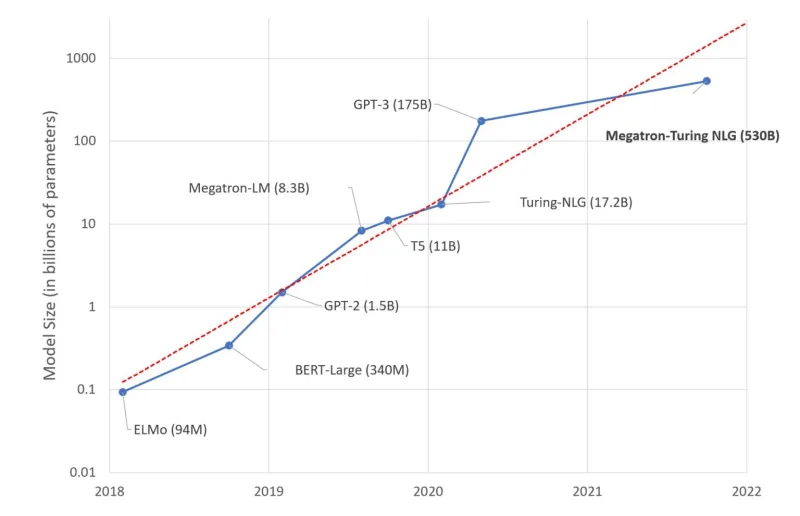
17th February 2022 AI may be "slightly conscious" The Chief Scientist and Co-Founder of OpenAI, one of the leading research labs for artificial intelligence, has suggested that the latest generation of neural networks are large enough to be "slightly conscious". Ilya Sutskever has made several major contributions to the field of deep learning. This includes beta testing of GPT-3 prior to its release. In a 2020 paper, he and his team concluded that the language model, featuring 175 billion parameters, "can generate samples of news articles which human evaluators have difficulty distinguishing from articles written by humans." Since GPT-3's launch on 11th June 2020, many other language models have emerged, some with even greater capabilities. In October 2021, for example, Microsoft and NVIDIA teamed up to create Megatron-Turing NLG. With its 530 billion parameters (triple that of GPT-3), this achieved "unmatched" accuracy in a broad set of natural language tasks.
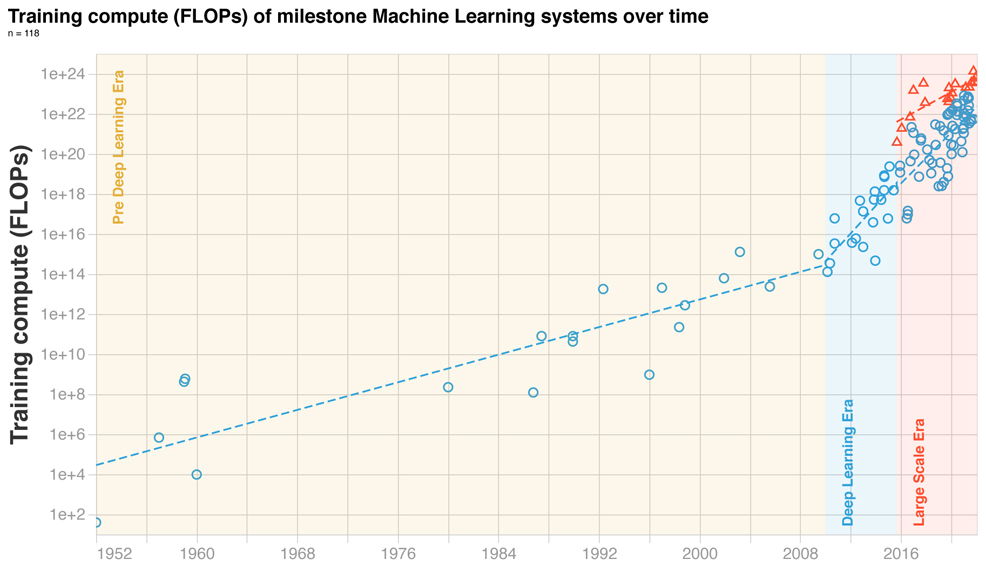
As to the question of whether such programs are edging towards an early form of consciousness, Sutskever's recent statement on Twitter prompted criticism and ridicule from many. However, some experts defended the idea – including MIT computer scientist Tamay Besiroglu, who tweeted: "Seeing so many prominent ML [machine learning] folks ridiculing this idea is disappointing. It makes me less hopeful in the field's ability to seriously take on some of the profound, weird and important questions that they'll undoubtedly be faced with over the next few decades." Besiroglu has just co-authored a new paper on the current state of machine learning (ML). No mention of consciousness appears in the study. It does, however, contain some eye-opening graphs, revealing extraordinarily rapid growth in the compute level for training models. The authors write:
Credit: Besiroglu, et al. (February 2022)
The data has been made publicly available. More than 100 machine learning systems are included, from as far back as 1952. Megatron-Turing NLG, the highest ranked entry, is shown to require 1024 FLOPS to train, 100 million times more than those of just a decade ago. The industry is now preparing for even greater leaps in orders of magnitude. Cerebras Systems, a California-based developer of semiconductors and AI, last year announced a new system that could soon enable the running of 120 trillion parameters on a single computer. That model size is roughly equivalent to the number of synapses in the human brain. Arguments will continue to rage about what constitutes "consciousness" – and whether AI is at an inflection point – but few would doubt that the field has seen significant advances in recent years. Next-generation neural networks, such as the expected successor to GPT-3, will further intensify that technological and philosophical debate.
Comments »
If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it:
|