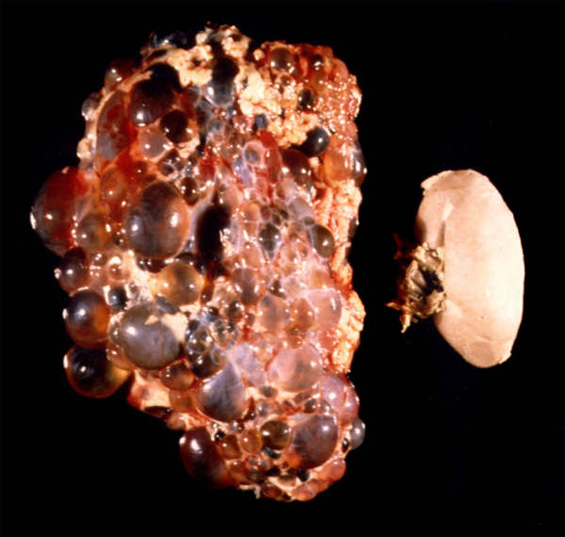
Cystic kidney growth curbed 5th November 2012 One of the most common life-threatening genetic illnesses, polycystic kidney disease affects more than 12.5 million people worldwide. Previously, only the symptoms could be treated. Now, researchers from the University of Zurich have succeeded in curbing the growth of these cysts in humans.
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common genetic disorders, affecting one in every 500 people and responsible for 10 percent of patients on dialysis worldwide. It is characterised by the growth of cysts that lead to progressive kidney failure and necessitate dialysis or a kidney transplant in most patients aged around fifty. Moreover, the persistent cyst growth causes high blood pressure and painful complications. Although we have known about the disease for over a century and its genetic basis for almost 20 years, there was no effective treatment until now. Kidneys stopped growing “Our study highlights a potential treatment that reduces kidney growth and the associated symptoms and slows the decline in kidney function,” explains Professor Olivier Devuyst – one of the chief researchers in the phase-three clinical trial just published in the New England Journal of Medicine. 1,445 patients were given tolvaptan over a three-year period at 129 centres worldwide. The drug is a selective V2 vasopressin receptor antagonist that lessens the effect of the antidiuretic (urine-concentrating) vasopressin hormone and increases urination. The researchers studied whether tolvaptan slows the progression of the kidney disease by slowing the cyst growth. “The study achieved its goal,” explained Professor Devuyst. In patients who received tolvaptan for three years instead of the placebo, the entire kidney volume decreased by nearly 50 percent, with fewer complications resulting from the disease, the pain eased off and the decline in kidney function was slowed. 15-year research project The study is the culmination of 15 years of research done by several research groups including that of Olivier Devuyst. They began by examining transport mechanisms in cells that coat the cysts and, in particular, identified the pathway of the V2 vasopressin receptor as a potential trigger for cystic kidney disease. The demonstration that blocking this receptor slows the disease and improves the kidney function in various animal models provided the rationale for the intervention study with tolvaptan.
Comments »
|